Using RFID For Warehouse Management System
RFID stands For “Radiofrequency Identification”.
RFID technology uses radio waves to automatically identify and track objects. RFID tags, which can be embedded in items like books, animals, vehicles, products, and even people, communicate with a reader to provide information about the tagged object. This data can then be used by a connected computer or network to monitor the object's location and movement. RFID is commonly used in inventory and warehouse management, supply chain management, and security systems.
In inventory and warehouse management, RFID tags are attached to items to be tracked. An RFID reader emits radio waves, and when a tagged object is within range, the tag sends back a signal to the reader. Unlike barcodes, which require line-of-sight scanning, RFID can identify objects without direct visual contact as long as they are within the reader's range.
Interested in learning how RFID can enhance your inventory management and ERP systems? Schedule a meeting with our ERP experts to discuss the benefits and get your questions answered. Improve your business operations and stay ahead of the competition with RFID technology in your warehouse.
Using RFID Technology Track Multiple Objects at the Same Time:
RFID System Contains 2 Components,
- RFID reader
- RFID tag
Different Types Of RFID Tags,
- Active tags
- Passive Tags
- Semi-Passive Tags
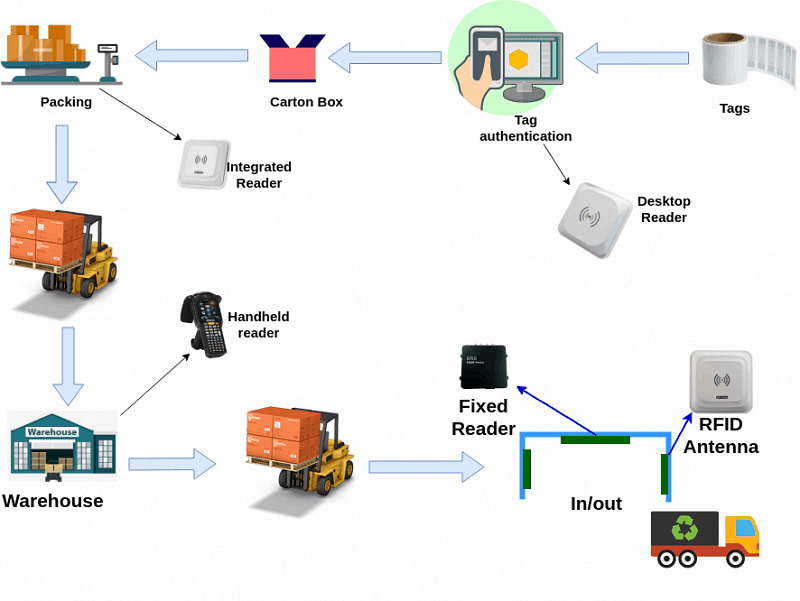
If it is a mobile handle-hold-like device, we will be using only a handled reader and an RFID tag for tracking.
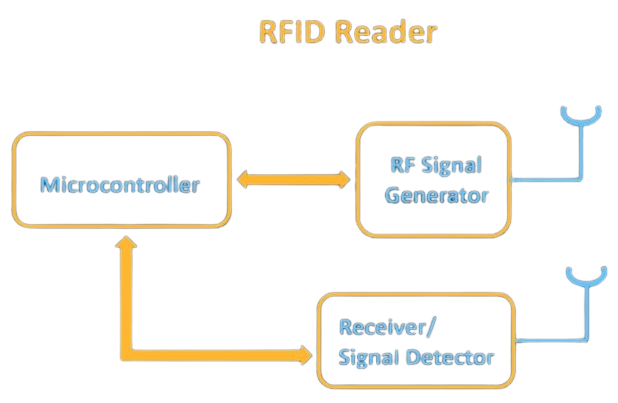
RFID Readers Mainly Consist of 3 Components
- RF signal generator – It generates the radio wave which is transmitted using the antenna. Also, receive the feedback signal which is coming from the tag.
- Receiver / Signal Detector – To process the information that is being sent by the RFID tag.
- Microcontroller – Many times this RFID reader is directly connected with the computer.
FREE Consultation to Implement RFID
How to Use RFID for Inventory Management in Large Warehouse Systems?
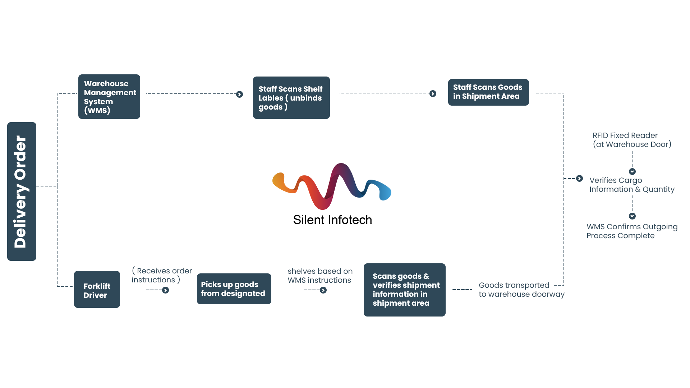
Outbound Process
- After the delivery order is received by the information, it is sent to the forklift truck.
- After the goods are off the shelves, the staff scan the electronic labels on the shelves to unbind the goods with the shelves.
- The staff scanned the goods in the shipment area and confirmed the shipment information.
- When the goods are transported to the doorway of the warehouse, the RFID fixed reader on the door of the warehouse checks the cargo information and quantity again.
- Completing the outgoing process after confirmation.
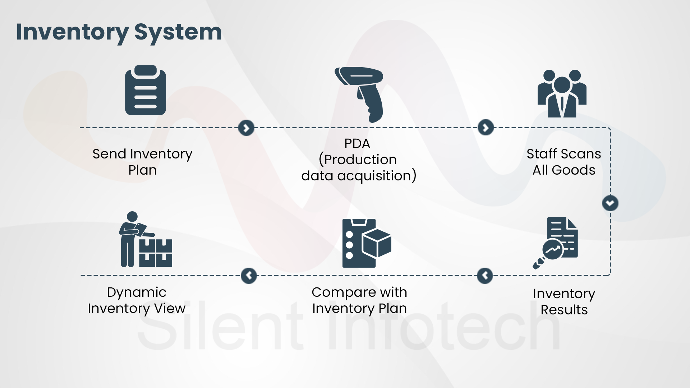
Inventory Process
- First, the system sends the inventory plan to the PDA(Personal Digital Assistant) handset.
- The staff can check the information about the goods by checking PDA.
- After receiving the instruction, the staff scan all the goods by mobile mode.
- Read all cargo information at one time.
- Record the inventory results synchronously and compare with the inventory plan to achieve dynamic inventory.
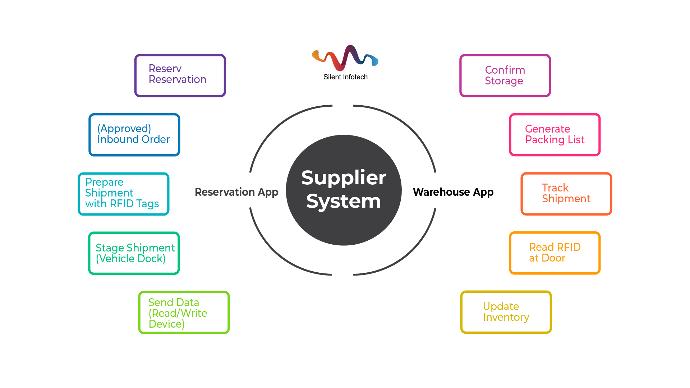
Inventory Inbound Process
- Supplier reserve the products through the application for reservation.
- Transfer through the system to the warehouse manager.
- After agreeing the supplier’s warehousing application the warehouse manager chooses to confirm the expected storage.
- Suppliers follow up the requirements, import the information by electronic tags and single phase correlation with shipments.
- The staff collates the information of the goods ready for shipment through the vehicle read-write device.
- The RFID reader installed at the door of the warehouse instantly reads out the goods and sends the information to the company.
- Achieve real-time dynamic management of supplier’s shipment information and confirm shipment information again.
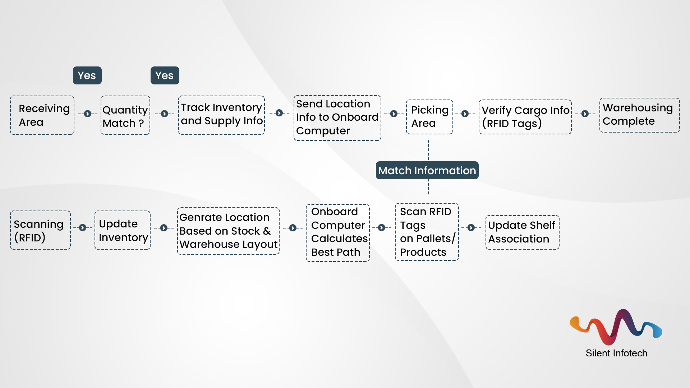
Warehousing Process
- After goods enter the storage area, the staff scan the goods in the storage area.
- If quantity and excepted quantity are kept, the next step will continue.
- The system follows up stocks and supply information and lays down the location of goods.
- And sends the information to the onboard computer to indicate the best path.
- After the goods are mounted, scan the RFID labels on the track and check the cargo information.
- Information has been associated with the shelves to completes the warehousing process, to achieve the synchronization of checking location.
Get FREE Consultation On Implementing RFID Inventory Management in WMS
Benefits of RFID For Inventory & Warehouse Management Software
- Allows individual stock items to be traced, located, and retrieved without human intervention.
- RFID chip system monitors the stocks 24/7.
- Automatically identifies stock levels to check for when recording is required.
- User time for manual recording can be reduced.
- Provides a more accurate system and eliminates human errors.
- The company will benefit from fewer errors in ordering costs and so save money.
- Many RFID tags can be read at once.
- This saves time because of whole pallets of products can be checked simultaneously.
- Tags can be overwritten – the information can be changed.
- This enables to be updated, for example when the stock is moved from one side of a store to another.
- Security of stock is increased.
- Tag readers can be placed at exits so that if stock is moved without authority it triggers the alarms.
- It can help to save money.
- RFID tags can prevent over-stocking on items such as perishable goods that have a short shelf life.
- RFID technology at the point of sale can be used to monitor demand trends.
- This is so stores can use the information to predict what should be ordered or for similar products to be considered for sale.
Barcode-based Warehouse Management System - Explore Now
Barcode vs RFID Technology for Inventory Tracking
Barcode | RFID |
| The barcode system requires a line of sight for a read. | RFID uses radio waves to wirelessly transmit data between the RFID tag and the reader, allowing for non-line-of-sight scanning. |
| Barcode reader typically operates in a distance of 1 to approx 18 inches. | The RFID system can operate in distances greater than 100m. |
| Due to the line of sight requirement, the barcode system can only read a single barcode at a time. | RFID systems depending on certain types and/or flavors of systems can read anywhere from 10’s to 100’s tags simultaneously. |
| The quality of a barcode can deteriorate rapidly over a short amount of time resulting in failed read attempts. | RFID tags are typically more rugged and therefore have a longer life expectancy than barcode labels. |
| Barcode readers are only able to read information from the barcode label. | The RFID system has the ability to read and write to the RFID tags. |
| Today barcodes are found on almost every item and there are no privacy issues involved with its use. | RFID tags are more reusable and rugged as they are protected by a plastic cover. |
| Barcodes are a universal technology in that they are the norm for retail products; stores that own a barcode reader can process barcodes from anywhere in the world. | RFID contains high levels of security; data can be encrypted, password protected or set to include a ‘kill’ feature to remove data permanently. |
Case Study – RFID Based Inventory Management For Seafood Processing
We have developed the AI based seafood supply chain ERP system where the seafood supplier can trace and track the freshness and quality of seafood. We are providing supply chain planning, supplier scheduling, product configurator, order to cash, purchasing, inventory, warehousing, and shipment.
In this ERP, Seafood caught by the fisherman and is then tagged with RFID or QR Codes, this then gets transferred, and the sensors on the seafood transmit information in real time about location, time, date, etc.
ERP Integrated Sensor Dashboard for Seafood Warehouse.
FAQs Related to Inventory Tracking Using RFID & Warehouse Management Software With RFID
RFID inventory management is a system that uses radio frequency identification (RFID) technology to track and manage inventory in a warehouse or storage facility. It involves placing RFID tags on items, which can be read by RFID readers or scanners. These tags contain unique identifiers that allow for accurate and efficient tracking of inventory throughout the supply chain process.
RFID offers several advantages over traditional inventory management methods. It enables real-time and automated tracking of inventory, reducing the need for manual counting and data entry. RFID systems provide increased accuracy, speed, and visibility into inventory levels, leading to improved efficiency and reduced errors. Additionally, RFID technology can help optimize inventory replenishment, minimize stockouts, and enhance overall supply chain management.
Yes, RFID technology can be integrated with existing inventory management systems. Many RFID solutions provide compatibility with popular inventory management software, allowing for seamless integration. This integration enables the transfer of RFID-generated data into the existing system, enhancing visibility and enabling efficient inventory control and analysis.
RFID technology can be used to track a wide range of items or products. It is commonly employed in industries such as retail, manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare. From individual retail products, clothing items, and electronics to pallets, containers, and even vehicles, RFID can be applied to track and manage various types of inventory.
Implementing RFID inventory management can lead to significant cost savings. By automating inventory tracking and reducing manual labor requirements, businesses can save on labor costs. RFID technology also enables better inventory control, minimizing stockouts and overstock situations, which can result in reduced holding and carrying costs. Additionally, the improved accuracy and visibility provided by RFID can help prevent theft, loss, or misplaced items, further saving costs.
RFID technology helps reduce inventory errors by eliminating the need for manual data entry and reducing human error. The automated and real-time tracking provided by RFID improves inventory accuracy and minimizes discrepancies between actual stock and recorded data. This accuracy leads to more efficient order fulfillment, reduced stockouts, and better inventory replenishment decisions, ultimately improving overall operational efficiency.
The time it takes to deploy an RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) system for inventory and warehouse management can vary depending on several factors, including the size of the warehouse, the complexity of the system, and the level of integration required. Generally, the deployment timeline can range from a few weeks to several months,

Rajesh R
A seasoned IT Integrations and ERP Solution Architect boasts over a decade's expertise in revolutionizing business processes through cloud-based ERP and MIS software solutions. Proficient in leveraging avant-garde technologies such as Blockchain, Al, IoT, etc in crafting bespoke software solutions. His extensive background encompasses tailor-made software solutions across diverse industries like Sales, Manufacturing, Food Processing, Warehouse Operations→ and B2B Businesses. Rajesh excels in engineering and deploying enterprise-grade business software, playing a pivotal role in Business Solution Consulting and designing intricate software solution architectures for many Fortune 500 enterprises.
Schedule Consultation with Rajesh Schedule Now